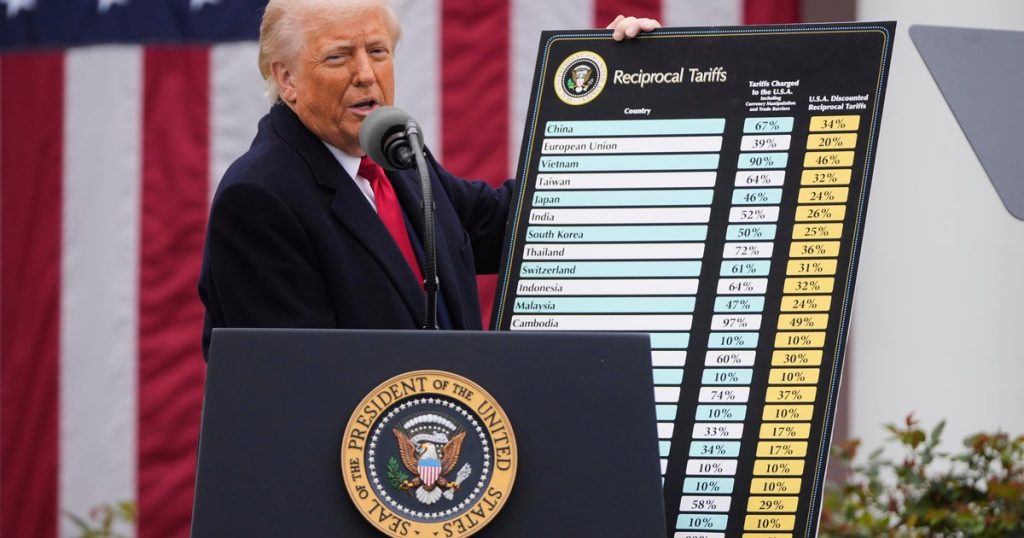
In a significant shift in trade policy, President Donald Trump announced a series of reciprocal tariffs targeting approximately 60 nations. This announcement, characterized by the president as “Liberation Day,” aims to address the longstanding trade deficits the United States has faced, particularly with countries like China and members of the European Union. Economists warn that these tariffs could reignite inflation and could provoke retaliatory measures from affected countries, potentially leading to broader economic ramifications.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) Overview of the Tariff Announcement |
| 2) Impact on Domestic and International Markets |
| 3) Timeline for Implementation of the Tariffs |
| 4) Justification Behind Tariff Rates |
| 5) Economic Predictions and Concerns |
Overview of the Tariff Announcement
On Wednesday, President Trump formally introduced new tariffs intended to stabilize the U.S. economy by addressing import imbalances. The president explained that a 10% blanket tariff would apply to all imports, alongside specific tariffs aimed at particular countries. In his remarks, he emphasized the need for fairness in trade relations: “Reciprocal. That means they do it to us, and we do it to them,” stated Trump. This reciprocal approach contributes to the overarching strategy of combating what he perceives as unfair trade practices that disadvantage American workers and manufacturers.
The tariffs have been met with mixed reactions from economists, some of whom argue they pose significant risks to both the U.S. economy and international trade relationships. As Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics, warned, if other nations respond with their own tariffs, it could lead to economic stagnation and recession in both the U.S. and abroad. The implications of these tariffs could reverberate through various sectors, affecting everything from job creation to consumer prices and international relations.
Impact on Domestic and International Markets
The tariffs are expected to have far-reaching effects on both domestic and international markets. Supporters of the tariffs argue that they will stimulate domestic manufacturing by shielding U.S. producers from foreign competition that has benefited from lower tariffs. This, they claim, will result in increased job creation within the manufacturing sector and lead to more robust economic growth.
However, critics caution that the immediate effect could lead to rising prices for consumers as companies pass on the costs associated with higher tariffs. Retailers and manufacturers relying on imports may face increased operational expenses, which could trickle down to consumers through inflated prices on goods. For example, industries such as electronics and automobiles that heavily depend on imported components may see price hikes, leading to reduced consumer spending and economic slowdown.
The international response to such tariffs is crucial, as affected nations may retaliate with their own tariffs on U.S. products. Such a tit-for-tat approach could foster a trade war, stalling global economic growth and negatively impacting any perceived benefits from the tariffs in the U.S. economy.
Timeline for Implementation of the Tariffs
The timeline for the tariffs’ implementation is critical in assessing their imminent impact. According to the announcement, the across-the-board 10% tariff will become effective at 12:01 a.m. on April 5, with the additional reciprocal tariffs set to be applied starting April 9. The phased rollout is intended to provide businesses time to adjust to the new tariff landscape and potentially explore alternative sourcing strategies to mitigate impending cost increases.
Business leaders and economists alike are closely monitoring the timeline, as rapid implementation could lead to shocks in the market and disrupt existing supply chains. Firms that rely heavily on imports against the backdrop of quickly imposed tariffs are scrambling to forecast cost adjustments and potential shifts in product pricing. Companies are assessing their operations to evaluate the impact on profit margins and are preparing for a possible resurgence in consumer prices.
Justification Behind Tariff Rates
During his announcement, President Trump outlined the rationale for the tariff rates by stating that they are designed to mirror the monetary levies imposed by other nations on U.S. imports. The administration conducted a thorough analysis of various countries’ tariffs and trade barriers to establish the specific rates, emphasizing that the new tariffs are only half of what those nations charge the United States.
“This is a kind approach,”
Trump remarked, suggesting that his administration is taking a moderate stance in comparison to existing rates.
By establishing tariffs in this calculated manner, the administration intends to leverage existing international trade disparities, compelling foreign nations to reassess their trade policies and potentially pave the way for new negotiations that could benefit U.S. interests. Nevertheless, critics of this strategy argue that it may ultimately feed into a cycle of retaliation, undermining the very economic stability the tariffs are designed to protect.
Economic Predictions and Concerns
Overall economic forecasts regarding the introduction of these tariffs yield a spectrum of concerns that have economists uneasy. Some experts, such as Mark Zandi, predict that if these tariffs remain in place long-term and lead to international retaliation, both the U.S. and its trade partners could experience serious recessions. The complexity of global trade networks means that tariffs could disrupt various industries, prompting layoffs and curtailing growth.
Inflation is another significant concern highlighted by economic experts. The introduction of tariffs generally leads to increased import prices, which could reignite inflationary trends that have remained subdued in the recent past. This situation would not only squeeze household budgets but could also lead the Federal Reserve to adjust its monetary policy which may further strain the economy. For consumers, the effects could manifest as increased prices on essentials, from food to clothing, leading to decreased discretionary spending.
In conclusion, while the intentions behind President Trump‘s tariff announcements may focus on rectifying trade imbalances and boosting domestic manufacturing, the potential for substantial economic fallout necessitates cautious evaluation and broad dialogue about future implications both domestically and globally.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | President Trump announced a 10% tariff on all imports, alongside reciprocal tariffs on 60 countries. |
| 2 | The tariffs aim to address U.S. trade deficits, particularly with China and the EU. |
| 3 | Implementation of the 10% tariff begins April 5, with reciprocal tariffs effective April 9. |
| 4 | The tariff rates were determined based on existing charges imposed by other countries on U.S. goods. |
| 5 | Economists express concerns about inflation and potential recessions arising from retaliatory measures. |
Summary
President Trump‘s recent tariff announcement marks a pivotal moment in U.S. trade relations, aiming to rectify perceived injustices in international trade. As businesses and economists prepare for implementation, the broader economic consequences remain uncertain. While intended to boost domestic production, these tariffs carry risks that could impact both consumer prices and global economic stability. Future discussions will likely center around the effects of these tariffs, not only on the national economy but also on international relations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What are reciprocal tariffs?
Reciprocal tariffs are duties imposed by a country on goods imported from another country that are equivalent to tariffs that country imposes on imports from the first country. For instance, if Country A charges 15% on imports from Country B, Country B may adopt a tariff of 15% on imports from Country A.
Question: How do tariffs affect consumers?
Tariffs can lead to higher prices on goods imported from countries that are subject to the tariffs. Businesses often pass these costs onto consumers, resulting in increased prices for everyday items, which can affect consumer spending in the economy.
Question: Why did President Trump implement these tariffs?
President Trump implemented these tariffs to address the U.S. trade deficit with other nations, specifically targeting countries with which the U.S. has significant trade imbalances. The administration’s goal is to boost domestic manufacturing and create a more equitable trade environment.