In 2025, measles outbreaks have sparked serious public health concerns, particularly in West Texas, where over 500 cases have been reported since January. Health officials emphasize that the majority of affected individuals, particularly children and teenagers, are unvaccinated. The emergence of these cases highlights the critical importance of vaccination as an effective preventive measure against this potentially deadly disease.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) Overview of the Texas Measles Outbreak |
| 2) Understanding the Dangers of Measles |
| 3) Identifying Measles Symptoms |
| 4) Vaccination Trends and Their Impact |
| 5) Recommendations for Measles Immunization |
Overview of the Texas Measles Outbreak
The ongoing measles outbreak in Texas has reached alarming proportions, with over 500 cases confirmed in a region primarily affecting unvaccinated children and teenagers since late January 2025. Local and state health officials have confirmed that nearly all those infected have either not received vaccinations or have an unknown vaccination status. This outbreak serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with vaccine hesitancy.
In February, a tragic incident occurred when a child died from complications associated with measles during this outbreak. This incident, alongside another death of an unvaccinated 8-year-old girl in early April, has raised concerns and highlighted the severe consequences of not getting vaccinated. These incidents of fatality underscore the critical need for increased immunization among children to prevent further loss of life.
Measles has since spread to over 20 other states, including neighboring New Mexico, New Jersey, and California. An alarming report also emerged from New Mexico where an unvaccinated adult tested positive for measles posthumously, though the official cause of death remains under investigation. Taken together, these incidents illustrate the need for heightened public awareness and action regarding measles vaccinations.
Understanding the Dangers of Measles
Measles is known to be highly contagious and can pose severe health risks, particularly for unvaccinated individuals. According to public health research, 1 in 5 unvaccinated people who contract the virus require hospitalization. Furthermore, severe complications can arise, including encephalitis, which can lead to brain damage, and even death in extreme cases. Historical records reveal that prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, thousands of cases resulted in fatalities each year.
The measles virus can be easily transmitted through the respiratory route, rendering it airborne and extremely infectious. In fact, nearly 90% of unvaccinated individuals exposed to the virus will contract the disease. Health experts advocate for vaccination to counter these risks effectively. The Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine provides a safe and reliable means of protection, significantly reducing the likelihood of infection and its associated severe complications.
Identifying Measles Symptoms
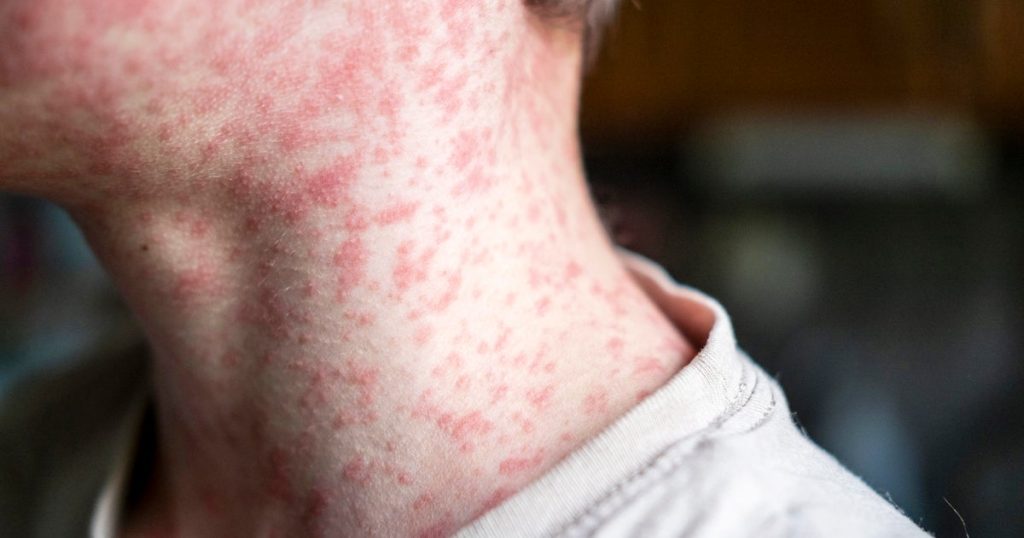
Symptoms of measles typically manifest about seven to 14 days after exposure to the virus. The initial symptoms are often mild and resemble those of other common viral infections, which include fever, cough, runny nose, and red eyes. Notably, a distinctive rash develops a few days after these initial symptoms, which can be a further indication of measles infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the fever associated with measles can spike to 104 degrees Fahrenheit. Serious complications may arise, such as pneumonia, which is noted as the most common cause of death from measles in young children. These complications highlight the importance for parents and caregivers to recognize the symptoms early for prompt medical intervention.
Dr. Lara Johnson, the chief medical officer at Covenant Children’s Hospital in Lubbock, Texas, reported that the hospital has seen numerous cases of confirmed measles, with severe cases requiring intensive care. This alarming trend underscores the critical need for community awareness and vaccination efforts.
Vaccination Trends and Their Impact
The increase in measles cases across the U.S. indicates a concerning trend in declining vaccination rates. Official data reveals that a significant portion of individuals affected during the Texas outbreak were unvaccinated or possessed unknown vaccination statuses. Health officials cite the link between lower vaccination rates, particularly in certain locales, and the resurgence of measles cases, posing a preventable public health crisis.
Dr. Amesh Adalja, an infectious disease physician, noted that the patterns of vaccination exemptions correlate significantly with rising case incidence. Areas with the lowest vaccination rates have been associated directly with outbreaks, resulting in hospitalizations for infected individuals. Such patterns indicate the severe impact of declined vaccination rates on community health.
Recent data indicates that at least ten states in the U.S. have reported declines in childhood vaccination rates, compromising the herd immunity needed to curtail outbreaks. This trend necessitates immediate action to boost vaccination rates and educate communities on the importance of vaccination for protecting against infectious diseases.
Recommendations for Measles Immunization
Public health experts recommend a two-dose regimen of the MMR vaccine for children to prevent measles. The first dose is advised between 12 to 15 months of age, with a second dose administered between 4 to 6 years old. The MMR vaccine has been proven through research to be highly effective; one dose is 93% effective against measles, while two doses provide 97% efficacy.
Despite being easily accessible, a concerning 17% of parents reported they have opted to skip or delay vaccination doses for their children. This figure reflects an increase from about 10% two years prior, emphasizing the growing challenges public health officials face in combating misinformation and vaccine hesitancy. Efforts to alleviate parental concerns and provide transparent information about vaccines are critical to rebuilding trust in vaccination programs.
Health officials emphasize the importance of confirming vaccination status. For those uncertain about their vaccination history, receiving an additional dose of the MMR vaccine poses no risk and is recommended as a precautionary measure.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | Over 500 measles cases were confirmed in West Texas since January 2025. |
| 2 | Majority of patients were unvaccinated children and teenagers. |
| 3 | Measles poses severe health risks, including death, particularly for unvaccinated individuals. |
| 4 | Symptoms appear 7 to 14 days post-exposure and include fever, cough, and rash. |
| 5 | Public health officials recommend routine vaccination to prevent measles outbreaks. |
Summary
The ongoing measles outbreak in Texas highlights the critical necessity for vaccination to prevent severe health consequences associated with this disease. The increased incidence among unvaccinated populations provokes concern among public health officials, emphasizing the need for comprehensive vaccination programs and robust educational campaigns to counter misinformation. With the proper preventive measures in place, measles outbreaks can be controlled and ultimately eradicated.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Why is measles considered highly contagious?
Measles is classified as highly contagious because it can be transmitted through respiratory droplets. An infected person can spread the virus to others even before symptoms appear, making it easier for outbreaks to occur, particularly in unvaccinated populations.
Question: What are the common side effects of the MMR vaccine?
The common side effects of the MMR vaccine are typically mild and may include fever, rash, or soreness at the injection site. Serious side effects are rare, and the vaccine has a strong safety record.
Question: How do health officials respond to declining vaccination rates?
Health officials respond to declining vaccination rates by implementing public awareness campaigns, providing accessible vaccination services, and engaging communities in discussions to address vaccine hesitancy. These efforts aim to educate parents about the importance of vaccination in preventing outbreaks.