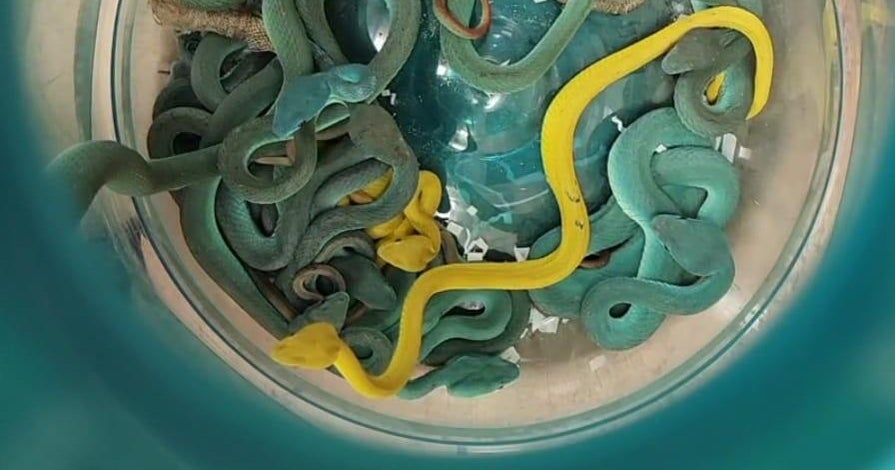
In a striking incident at Mumbai’s Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport, Indian customs officials apprehended an individual trying to smuggle dozens of dangerous snakes into the country. The smuggled cargo consisted of 44 Indonesian pit vipers, alongside three Spider-tailed horned vipers and five Asian leaf turtles. The arrest, which took place as the flight arrived from Thailand, highlights ongoing issues surrounding wildlife trafficking and illegal smuggling operations.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) The Discovery of Smuggled Species |
| 2) Arrest of the Suspect |
| 3) Historical Context of Wildlife Smuggling in India |
| 4) Recent Cases of Wildlife Trafficking |
| 5) Legal Implications and Consequences |
The Discovery of Smuggled Species
On June 1, 2025, customs officials at Mumbai Airport uncovered an alarming variety of smuggled reptiles hidden within a passenger’s checked baggage. The illegal cargo primarily consisted of 44 Indonesian pit vipers, species well-known for their potent venom and predatory nature. Alongside these, the customs team also discovered three Spider-tailed horned vipers, which, while venomous, primarily prey on smaller animals such as birds. The package also included five Asian leaf turtles, a species that is often targeted in wildlife trafficking.
Such discoveries pose significant ecological concerns, as smuggling not only threatens the species involved but may also disrupt local ecosystems. Reports from Mumbai Customs reflect growing efforts to combat wildlife trafficking, which has become increasingly sophisticated in recent years. This incident underscores the persistent threat posed by illegal wildlife trade that endangers biodiversity worldwide.
Arrest of the Suspect
An Indian national was promptly arrested following the discovery of the smuggled snakes at the airport. Customs officials described the individual as an experienced smuggler who had concealed the reptiles in checked luggage. Authorities apprehended the suspect during routine security checks. Such arrests are crucial for breaking the cycle of wildlife trafficking and serving as a deterrent to would-be smugglers.
In the statement released by Mumbai Customs, they confirmed the arrest and underscored the importance of vigilance in thwarting illegal smuggling operations. This apprehension aligns with many other successful operations aimed at safeguarding endangered species and enforcing stricter punishments for traffickers.
Historical Context of Wildlife Smuggling in India
India’s rich biodiversity makes it a hotspot for wildlife trafficking, with various exotic species like snakes, birds, and mammals being targeted. Customs data indicates that incidents involving the smuggling of wildlife have been on the rise, reflecting a growing threat to conservation efforts. Wealthy and organized syndicates are often behind these operations, making it increasingly challenging for authorities to completely curb this illegal trade.
The problem is not merely localized; it is part of a global network where animals are frequently trafficked across international borders. India serves as both a source and a transit point for wildlife, often trading animals with countries in the region and beyond. The ramifications of this illicit trade extend beyond ecological concerns, impacting public health and safety as well.
Recent Cases of Wildlife Trafficking
Wildlife trafficking continues to be a pressing issue at Mumbai Airport, with customs officials having dealt with multiple significant cases over the past year. Earlier investigations led to the capture of five endangered Siamang gibbons, ingeniously concealed in a plastic crate within a passenger’s baggage. Such ruthlessness highlights the determination of traffickers to illegally trade endangered species.
In another incident, a passenger was detained with 12 live turtles concealed in their bag, while another case involved the smuggling of four hornbills. Both incidents reaffirm the serious nature of wildlife trafficking in India and demonstrate that the authorities are becoming increasingly adept at uncovering these hidden smuggling operations.
Moreover, recent arrests included individuals attempting to transport juvenile caimans, further proving that traffickers will exploit virtually any species for profit.
Legal Implications and Consequences
The legal framework surrounding wildlife smuggling in India is governed by various laws including the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, and regulations under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). The apprehended individual faces serious charges that could result in stiff penalties, including lengthy prison sentences, heavy fines, and confiscation of assets related to the illegal activity.
Increased awareness and stringent laws have prompted authorities to take harsher actions against offenders. Convictions often send a strong message, discouraging aspiring traffickers from engaging in illegal wildlife trade. The legal measures aim not only to punish offenders but also to protect vulnerable species and preserve ecological balance.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | Indian customs officials apprehended an individual smuggling 44 Indonesian pit vipers and other reptiles into Mumbai from Thailand. |
| 2 | The suspect was caught during routine security checks and faces serious legal repercussions. |
| 3 | Wildlife trafficking remains a significant issue in India, prompting authorities to take strict measures against offenders. |
| 4 | The incident highlights ongoing challenges surrounding the protection of endangered species and ecological balance. |
| 5 | Increased awareness and stricter laws aim to deter wildlife trafficking operations across the country. |
Summary
This recent incident at Mumbai Airport sheds light on the ongoing battle against wildlife trafficking and illegal smuggling in India. With growing instances of animal smuggling, it is crucial for authorities to remain vigilant and take decisive measures to protect endangered species. The apprehension of the suspect reflects not only the efforts of customs officials but also the need for collective action to address and mitigate the complexities surrounding wildlife conservation and trafficking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What types of animals are most commonly smuggled?
Commonly smuggled species include various reptiles, birds, and mammals, with particular focus on exotic and endangered species due to their high market value.
Question: What penalties do wildlife traffickers face in India?
Wildlife traffickers in India can face severe legal consequences, including prison sentences, hefty fines, and the confiscation of any assets linked to their illegal activities.
Question: How does wildlife trafficking impact biodiversity?
Wildlife trafficking threatens biodiversity by reducing populations of vulnerable species, disrupting ecosystems, and altering the natural balance between various species in their habitats.