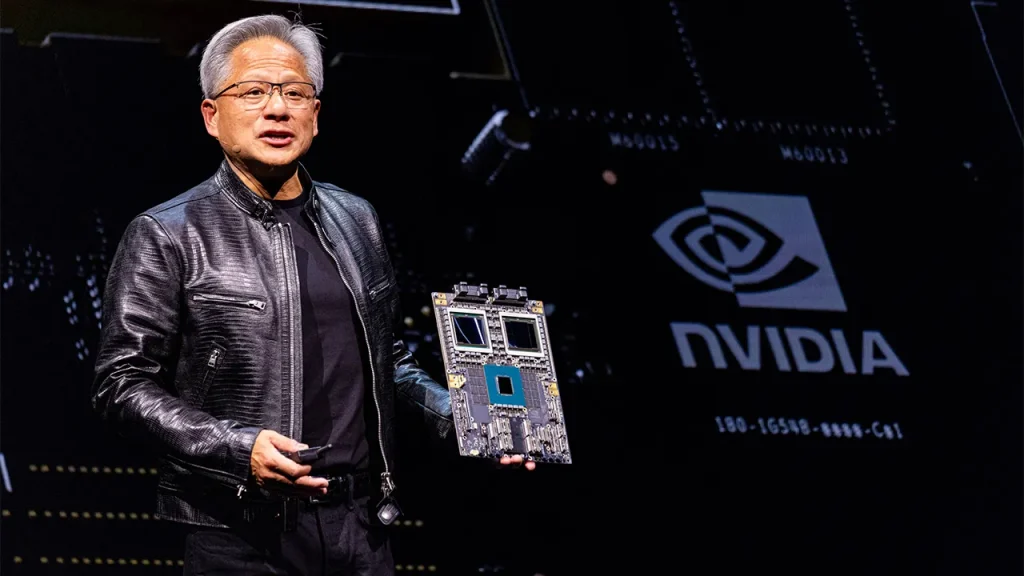
In a groundbreaking announcement on Monday, tech giant Nvidia revealed plans to manufacture artificial intelligence supercomputers in the United States for the first time. This move comes as the company seeks to bolster its domestic production capabilities amidst increasing demand for AI technologies. Alongside Nvidia’s news, advancements in robotics were highlighted, including robots designed for dairy farming and an innovative, hydrogen-powered robotic horse prototype, showcasing the wide-ranging potential of AI and robotics across various industries.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) Nvidia’s Pioneering AI Supercomputers |
| 2) Revolutionizing Dairy Farming with Robotics |
| 3) CORLEO: The Rideable Hydrogen-Powered Robot |
| 4) The Rise of Service Robotics in Various Sectors |
| 5) Implications of Automation in Employment |
Nvidia’s Pioneering AI Supercomputers
Nvidia has announced its intention to manufacture AI supercomputers entirely within the United States, marking a significant milestone in the tech industry. The company, founded by Jensen Huang, aims to leverage American manufacturing capabilities to meet the growing global demand for sophisticated AI processing power. This strategy will see Nvidia produce its advanced systems in U.S. facilities, increasing operational transparency and strengthening domestic supply chains.
The decision to move production to the U.S. is partly influenced by recent geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities exposed by global crises. By establishing manufacturing operations in the U.S., Nvidia is not only adhering to the national push for technological independence but also seeking to bolster job creation in the tech sector. The initiative reflects a broader trend among major tech companies to domesticate supply chains, ensuring they are less reliant on overseas production.
As part of this venture, Nvidia plans to invest significantly in cutting-edge production technologies that will support the creation of highly efficient AI supercomputers. This initiative is anticipated to have far-reaching impacts on various industries, enhancing capacities for data processing, machine learning, and faster technology deployment across sectors including healthcare, finance, and automotive.
Revolutionizing Dairy Farming with Robotics
The innovation in dairy farming has taken a notable leap forward with the introduction of robotic systems designed to milk cows. These robots automate the milking process while also tending to the cows’ welfare, creating a stress-free environment that promotes higher yields. As dairy farmers wrestle with labor shortages and the need for operational efficiency, such robotic solutions have become increasingly appealing.
Robots in dairy farms are not just performing manual tasks; they are equipped with advanced sensory technologies that monitor the health and well-being of the livestock. This integration of technology allows farmers to collect data that can lead to improved herd management and productivity. The use of robotics in agriculture showcases a shift towards more sustainable farming practices, emphasizing efficiency while addressing the pressing need for food security.
By optimizing the milking process and reducing stress among animals, these robotic systems present a dual solution: meeting increased dairy production demands while supporting animal welfare standards. This development has caught the attention of the agricultural sector, which now sees technology as a necessary partner in navigating future farming challenges.
CORLEO: The Rideable Hydrogen-Powered Robot
In a groundbreaking display of engineering, Kawasaki Heavy Industries has unveiled CORLEO, a hydrogen-powered, four-legged robot that is designed for human riders. This innovative prototype represents the intersection of robotics and mobility, promising not only functionality but also sustainability through its hydrogen fuel source. The design of CORLEO is reminiscent of fantastical elements often seen in video games, creating excitement and intrigue around its capabilities.
With a focus on providing an alternative mode of transportation, the development of this rideable robot highlights ongoing research into vehicle automation and personal mobility solutions. The hydrogen-powered aspect signifies a growing shift towards environmentally friendly technologies that aim to reduce carbon emissions associated with traditional vehicles. By utilizing hydrogen as a fuel source, Kawasaki not only presents a novel mode of transport but also contributes to the movement towards sustainable energy solutions.
As the prototype progresses through development phases, it promises to bring about discussions on infrastructure needs and the feasibility of integrating such robots into everyday life. The potential of a rideable robot could redefine personal transportation, merging convenience with eco-friendly technology.
The Rise of Service Robotics in Various Sectors
The field of service robotics continues to expand as new technologies emerge, particularly those capable of handling complex tasks in industries like hospitality, healthcare, and retail. One of the standout innovations is the FlashBot Arm, a semi-humanoid robot developed to perform various tasks traditionally completed by human workers. With its advanced manipulation capabilities and intelligent delivery features, the FlashBot Arm is poised to transform how services are delivered in critical sectors.
Service robots are designed not only to perform repetitive tasks but also to interact with their environments in ways that mimic human behavior. This anthropomorphic approach allows robots to engage more effectively with customers and clients, fostering a smoother operational workflow in settings like restaurants and hospitals. The adoption of such robotics solutions is indicative of a broader recognition of the efficiencies they bring to service industries, especially in the face of labor shortages or high turnover rates.
The growing prevalence of service robotics raises essential questions about the future of work. As businesses increasingly rely on these technologies to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences, discussions around the potential displacement of human workers become more pressing. It is vital for stakeholders across sectors to navigate these challenges thoughtfully while considering the advantages of integrating robots into the workforce.
Implications of Automation in Employment
With the rise of AI and robotics, the dialogue around employment implications continues to intensify. As companies introduce more sophisticated automation in their operations, concerns about job displacement have become a central theme. The transition toward automated systems, while offering efficiency and cost-saving benefits, confronts workers with the challenge of adapting to new technological contexts.
Experts debate the consequences of automation. On one hand, advancements in technology empower workforces with tools that enhance productivity and ease in workload management. On the flip side, the fear of job loss looms large, particularly in sectors with routine tasks that can be automated. Sectors like manufacturing, hospitality, and even service industries face the potential for significant disruption.
As organizations forge ahead with integrating robots and AI into their operations, it becomes imperative for policymakers and educational institutions to facilitate reskilling and upskilling initiatives. By providing pathways for workers to transition into new roles, the integration of advanced technologies can lead to a redefinition of labor rather than outright loss.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | Nvidia plans to manufacture AI supercomputers in the U.S., helping to bolster domestic production. |
| 2 | Robotic systems in dairy farming enhance productivity and animal welfare. |
| 3 | Kawasaki’s CORLEO offers a sustainable, rideable robotic option powered by hydrogen. |
| 4 | Service robots, including the FlashBot Arm, are transforming roles in various industries. |
| 5 | The rise of automation prompts discussions on employment impacts and workforce adaptation. |
Summary
The announcement from Nvidia reflects a significant shift in the tech landscape towards domestic manufacturing and innovation in AI technologies. As robotics technology progresses, industries ranging from agriculture to transportation are undergoing transformative changes, addressing both operational efficiency and sustainability in their practices. However, as these advancements unfold, it is crucial to consider the socio-economic implications of automation, particularly on employment. The ongoing developments in AI and robotics present opportunities and challenges that will shape the future of industries worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What are Nvidia’s plans for AI supercomputers?
Nvidia plans to manufacture its AI supercomputers entirely in the U.S. to enhance domestic production capabilities and meet the growing demand for advanced AI technologies.
Question: How are robots improving dairy farming?
Robots in dairy farms are automating the milking process and monitoring cow health, creating a more efficient and stress-free environment for the livestock.
Question: What is the significance of Kawasaki’s CORLEO?
CORLEO is a hydrogen-powered robotic horse prototype designed for human riders, showcasing advancements in mobility technology and the push for sustainable energy use.