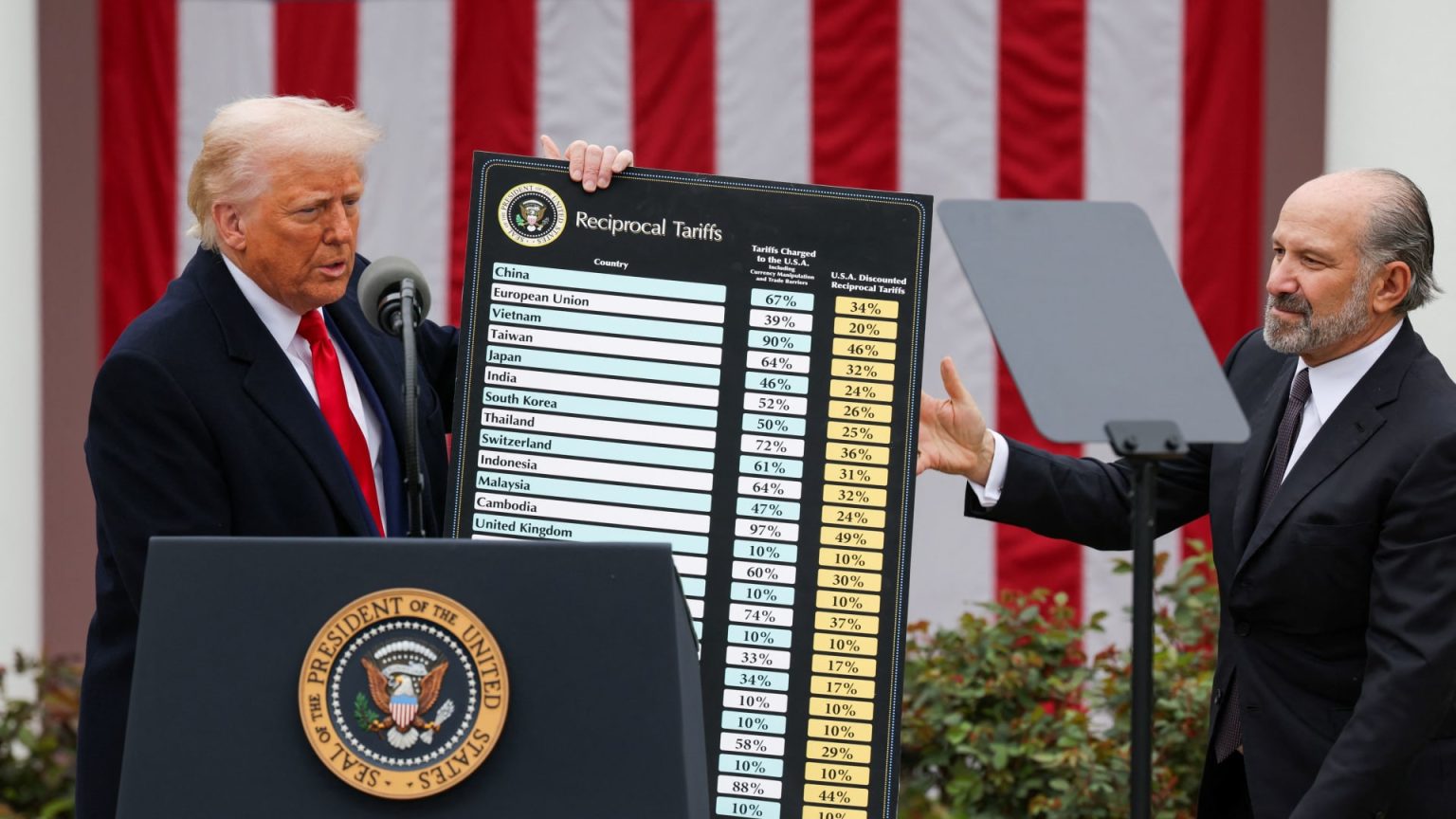
In a significant development regarding U.S. trade policy, Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick expressed on Sunday that the 10% baseline tariff on imports is set to persist for the foreseeable future. His remarks align closely with statements made by President Donald Trump in recent days. This decision, which aims to balance the trade dynamics with foreign countries, has sparked concerns about its potential impact on consumer prices, particularly as businesses may seek to pass increased costs onto consumers in the wake of these tariffs.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) Commerce Secretary’s Confirmation of Tariff Stability |
| 2) Implications for Consumers and Businesses |
| 3) Recent Trade Agreements and Their Context |
| 4) Future Prospects for Tariff Changes |
| 5) Overall Economic Impact and Analysis |
Commerce Secretary’s Confirmation of Tariff Stability
On a recent broadcast of ‘State of the Union,’ Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick confirmed that the 10% baseline tariff on imports from various countries would likely remain intact in the foreseeable future. This assessment is in alignment with remarks made by President Donald Trump earlier, suggesting a consistent approach to the nation’s trade policy. Lutnick emphasized during the interview that such tariffs are not merely temporary measures but a key part of a broader strategy aimed at reshaping international trade.
Lutnick remarked, “We do expect a 10% baseline tariff to be in place for the foreseeable future,” signaling a more defined pathway for U.S. trade relations. The commitment to maintaining the tariff comes during a period characterized by global economic uncertainty, exacerbated by various geopolitical tensions. The secretary underscored that these tariffs are not meant to penalize consumers but are intended to encourage competition from domestic producers and make foreign goods more accountable in pricing.
Implications for Consumers and Businesses
Despite Lutnick’s assurances, there are growing concerns regarding the potential financial repercussions for American consumers. Data suggests that businesses may attempt to transfer the increased costs associated with tariffs onto consumers, resulting in higher prices for household items. Reports indicate that consumer confidence has declined substantially following the announcement of these tariffs on April 2, 2025.
Economic analysts argue that while Lutnick insists the burden will primarily fall on businesses and foreign suppliers, the reality is that consumers often bear the brunt of such policies. “Businesses, their job is to try to sell to the American consumer,” Lutnick stated, emphasizing the issue of competition. This suggests that while tariffs aim to protect domestic industries, they may inadvertently lead to increased costs for everyday consumers as companies adjust their pricing strategies in response to tariff policies.
Recent Trade Agreements and Their Context
In the backdrop of this announcement, it is important to consider the recent trade agreement reached between the United States and the United Kingdom. The deal has generated considerable discussion, particularly as it relates to how the 10% baseline tariff will be applied moving forward. Although President Trump described the tariff as a “low number” in the context of the U.K. trade deal, he also indicated that some tariffs could be “much higher” for certain other countries with which the U.S. has significant trade surpluses.
Trump further emphasized that such thresholds could vary based on the unique economic relationships the U.S. holds with different nations. This indicates a flexible approach to tariffs while maintaining a base level, thereby creating a dynamic trade environment that could shift based on negotiations and trade balances with specific countries.
Future Prospects for Tariff Changes
Looking ahead, the situation regarding tariffs remains fluid, with potential for adjustments depending on the outcomes of upcoming trade negotiations. The administration appears committed to using tariffs as leverage in international trade dealings, especially when engaging with nations that exhibit large trade surpluses with the U.S.
Industry experts are weighing in on what these developments could mean for the future of U.S. trade policy. Some analysts suggest that while the intent behind the baseline tariff is to reinforce domestic manufacturing, it may also prompt retaliatory measures from other nations, potentially leading to a trade war. The balance between encouraging domestic growth and mitigating international trade tensions will be critical in guiding future tariff decisions.
Overall Economic Impact and Analysis
The ongoing dialogue surrounding tariffs is not merely a question of economic policy, but also touches on broader societal implications. As consumer prices fluctuate in response to imposed tariffs, the potential impact on household budgets could shift spending patterns in significant ways. As a result, this could hinder economic growth, as consumers may turn to savings over spending.
Moreover, the effectiveness of tariffs as a tool for economic improvement remains a subject of debate among economists. Some argue that while tariffs may protect domestic industries in the short term, they may also lead to inefficiencies and higher prices in the long term. Hence, as the administration moves forward with its tariff strategy, careful consideration will need to be given to the various economic indicators that emerge as a result of these policies.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | A 10% baseline tariff on imports is expected to remain in place for the foreseeable future, as confirmed by Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick. |
| 2 | Concerns are growing over how increased tariffs may affect consumer prices and overall consumer confidence. |
| 3 | Recent trade agreements, including one with the United Kingdom, will still see the application of the 10% baseline tariff. |
| 4 | Future tariff adjustments will likely hinge on trade negotiations with countries that have large trade surpluses with the U.S. |
| 5 | Tariffs may protect domestic industries, but they also risk causing increased consumer prices and potential retaliatory measures from other nations. |
Summary
The recent commentary from Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick on the expected permanence of a 10% baseline tariff highlights the U.S. administration’s ongoing commitment to using tariffs as a central strategy in its international trade policy. While aiming to bolster domestic manufacturing, the potential repercussions for consumers and the broader economy are significant. As trade relationships evolve and new agreements are formed, the administration will need to navigate the complexities of tariffs carefully to balance protectionist aims with economic growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is the purpose of the 10% baseline tariff?
The 10% baseline tariff is intended to protect domestic industries by making foreign goods more expensive, thereby encouraging consumers to buy American-made products.
Question: How does this tariff affect consumers?
Consumers may face higher prices for imported goods as businesses may pass on the costs associated with the tariff, potentially reducing consumer confidence and altering spending behaviors.
Question: Are there plans for future tariff changes?
Yes, the administration is open to adjusting tariffs based on individual trade negotiations and the economic relationships with different countries, especially those with significant trade surpluses with the U.S.