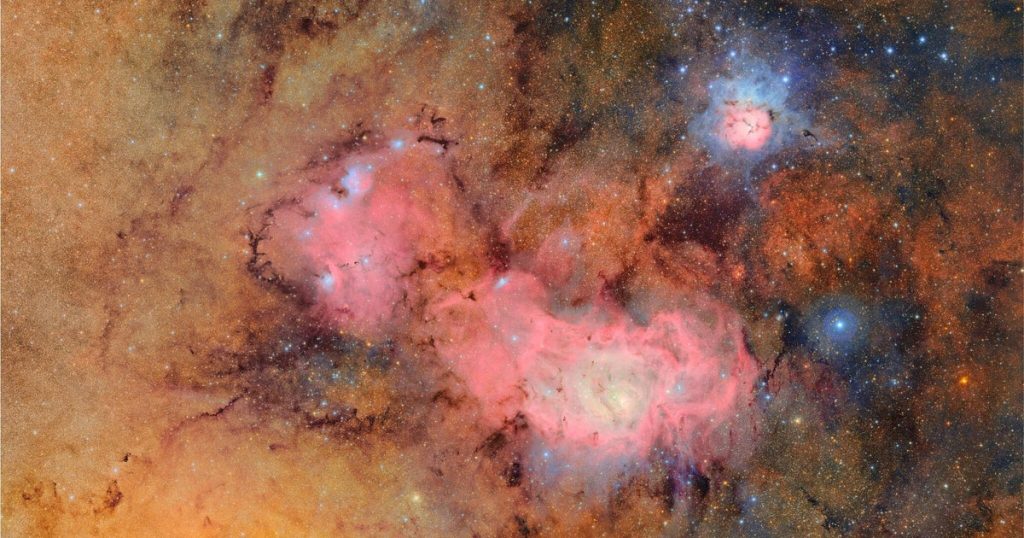This week marked a significant milestone in astronomical observation with the release of the first images from the highly anticipated Vera Rubin Observatory in Chile. Over 20 years in the making, this state-of-the-art facility houses the world’s largest telescope, designed to explore deep space and unravel cosmic mysteries. The initial images showcase stunning views of distant galaxies and star-forming regions, setting the stage for a decade of groundbreaking research.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) Overview of the Vera Rubin Observatory |
| 2) The First Images and Their Significance |
| 3) Key Objectives of the Observatory |
| 4) The Role of Dark Matter and Dark Energy |
| 5) Implications for Asteroid Detection and Future Research |
Overview of the Vera Rubin Observatory
The Vera Rubin Observatory, situated at the summit of Cerro Pachón in central Chile, represents a monumental leap in astronomical technology. Funded by the U.S., this facility has been the focus of scientific endeavors for over two decades. Its design capitalizes on the pristine conditions offered by the site’s dark skies and minimal atmospheric disturbance. With an advanced 8.4-meter telescope and the largest digital camera ever constructed, the observatory is poised to redefine our understanding of the cosmos.
Utilizing cutting-edge technology, the observatory aims to capture images with unprecedented clarity. Its strategic location allows astronomers to observe celestial phenomena that might otherwise be obscured by light pollution or atmospheric interference. This capability positions the Vera Rubin Observatory as a leading institution in the field of astronomy, capable of delivering insights that will challenge existing paradigms and fuel further inquiry.
The First Images and Their Significance
The unveiling of the first images taken by the Vera Rubin Observatory was met with excitement within the scientific community. Among these initial captures are stunning visuals of the Trifid Nebula and the Lagoon Nebula, located several thousand light-years from Earth.
“The images reveal stellar nurseries within our Milky Way in unprecedented detail,”
remarked a spokesperson, noting how features previously unseen are now accurately depicted.
Another mesmerizing image showcases the expansive Virgo Cluster of galaxies, emphasizing the scale and diversity of cosmic structures. The observatory also released a video presentation called the “cosmic treasure chest,” highlighting a staggering 10 million galaxies in a single panoramic view. These initial revelations underscore the potential of the observatory to capture intricate cosmic details, thereby enriching our understanding of the universe.
Key Objectives of the Observatory
One of the primary goals of the Vera Rubin Observatory is to understand the history and evolution of the universe. Commissioning scientist Elana Urbach emphasized the necessity for exceptionally sharp images to visualize events like supernova explosions that happened billions of years ago. This exploration into cosmic history aims to illuminate the fundamental processes that have shaped our universe and to gather invaluable insights into planetary formation and stellar cycles.
Later this year, the observatory will kick off its flagship initiative, the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). This extensive project will systematically scan the night sky each night over a span of ten years, allowing researchers to monitor transient changes in real-time. The LSST represents a significant commitment to advancing observational astronomy, with ramifications likely to extend beyond current scientific knowledge.
The Role of Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Integral to the observatory’s mission is the exploration of dark matter and dark energy, enigmatic components of our universe that account for approximately 95 percent of its total mass-energy content. The observatory is named in honor of Vera C. Rubin, whose pioneering research provided pivotal evidence for the existence of dark matter. The exploration of dark matter will enhance our understanding of gravitational dynamics within galaxies.
Similarly, dark energy, the force believed to be driving the accelerated expansion of the universe, poses significant questions for physicists and astronomers alike. The findings from the Vera Rubin Observatory are expected to contribute to an evolving framework that seeks to explain these mysterious components of the cosmos, enabling studies that may answer lingering questions about the universe’s fate and structure.
Implications for Asteroid Detection and Future Research
In addition to studying distant galaxies and cosmic phenomena, the Vera Rubin Observatory is already proving its value in tracking near-Earth objects, contributing significantly to planetary defense initiatives. Within just 10 hours of observation, the facility managed to identify 2,104 new asteroids, including several located near Earth. This accomplishment highlights its prowess in locating celestial bodies that pose potential threats to our planet. The capabilities of the observatory will surpass those of all other ground- and space-based observatories combined, which typically identify about 20,000 new asteroids annually.
As the observatory continues to refine its observational techniques, it stands to become even more efficient in spotting interstellar objects passing through our solar system. The implications of its findings may broaden our knowledge of celestial objects and their trajectories, improving not only our understanding of space but also enhancing our preparedness for potential extraterrestrial threats.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | The Vera Rubin Observatory is the world’s largest telescope for deep space observation, located in Chile. |
| 2 | The initial images captured stunning nebulas and galaxies, revealing details previously obscured. |
| 3 | The observatory aims to explore the universe’s history and expects to make significant discoveries over the next decade. |
| 4 | Research on dark matter and dark energy is a critical focus of the observatory’s mission. |
| 5 | The observatory is enhancing asteroid detection capabilities, crucial for planetary defense. |
Summary
The debut of the Vera Rubin Observatory heralds a new era in astronomical exploration, offering unprecedented insights into the cosmos. As it embarks on its ambitious ten-year plan, the observatory is positioned to answer key questions regarding the universe’s formation and composition, while simultaneously playing a vital role in tracking asteroids. The initial images provide a tantalizing glimpse into what is to come, reaffirming the importance of continued investment in scientific research and technological advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is the purpose of the Vera Rubin Observatory?
The purpose of the Vera Rubin Observatory is to explore the universe’s history, study dark matter and dark energy, and conduct extensive astronomical surveys over the next decade.
Question: How does the observatory enhance asteroid detection?
The observatory is equipped with advanced technology that enables it to detect previously unidentified asteroids, including near-Earth objects, significantly improving planetary defense efforts.
Question: What makes the initial images from the observatory significant?
The initial images reveal cosmic phenomena with unprecedented detail, providing insights into star formation and the structure of galaxies, which could reshape our understanding of the universe.