In a recent address to Congress, officials reported that President Trump reiterated his administration’s commitment to restoring U.S. control over Greenland and the Panama Canal. Trump emphasized the strategic and economic importance of these territories for national security, prompting significant reactions from leaders in both Greenland and Panama. This marked a continuation of Trump’s controversial stance on foreign territories, while raising questions about U.S. foreign relations and territorial sovereignty.
| Article Subheadings |
|---|
| 1) The Importance of Greenland in U.S. Strategy |
| 2) The Significance of the Panama Canal for U.S. Economy |
| 3) Reactions from Key Global Leaders |
| 4) Historical Context of U.S. Interests in Greenland |
| 5) The Historical Background of the Panama Canal |
The Importance of Greenland in U.S. Strategy
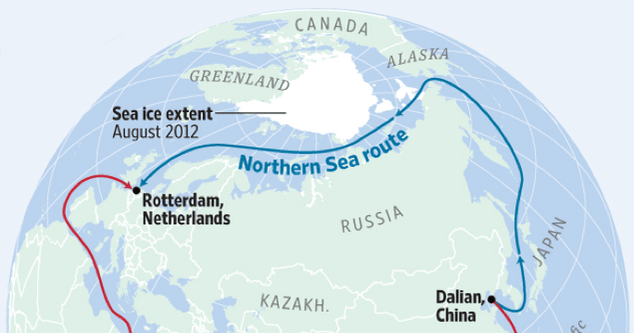
Greenland, the world’s largest island, is strategically located between North America and Europe, making it a significant asset for the U.S. This semi-autonomous territory, which is part of the Kingdom of Denmark, has been of increasing interest to the U.S. as global dynamics shift, especially in the Arctic region. The ongoing melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet due to climate change has revealed new shipping routes through the Arctic, making Greenland increasingly strategic for both military and economic interests.
President Trump has made it clear that he views Greenland as crucial for national security. During his address, he stated,
“We need Greenland for national security and even international security.”
This reflects broader concerns over the growing presence of foreign powers, particularly China and Russia, in the Arctic. As ships from these nations navigate through newly opened routes, there is a sense of urgency in the U.S. to maintain a strategic foothold in Greenland to oversee these activities.
Furthermore, Greenland is home to rich mineral resources, including oil, natural gas, and rare earth elements essential for modern technologies. According to recent reports, these resources remain largely untouched, presenting an opportunity for economic leverage. In this context, Trump’s administration seems poised to capitalize on tensions between Greenland and Denmark, as some experts suggest that these geopolitical relations could play to U.S. interests.
The Significance of the Panama Canal for U.S. Economy
The Panama Canal is a pivotal maritime trade route that connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, significantly shortening travel times for shipping between the two major bodies of water. Approximately 40% of U.S. container shipping traverses the canal, underscoring its importance to the American economy. Trump has claimed that restoring U.S. control over the canal is essential for “economic security,” even though it was fully handed over to Panama in 1999.
In his recent congressional speech, Trump falsely stated that the canal is currently being operated by China, a claim disputed by Panama’s President Jose Raul Mulino, who insisted that China does not control the canal. The misconception appears to stem from a broader narrative within the Trump administration regarding Chinese influence in Latin America. The president’s rhetoric suggests his desire to reclaim landmark assets for the U.S., which he believes would bolster national interests.
Additionally, recent developments have signaled a shift in Panama’s approach to foreign investments, particularly in its collaboration with Chinese companies. After a visit from U.S. officials, Panama opted not to renew a key infrastructure agreement with Beijing. Trump leveraged this moment to highlight an upcoming investment opportunity led by American firm BlackRock, reinforcing the notion that the canal should benefit American economic interests.
Reactions from Key Global Leaders
The remarks made by President Trump during his congressional address have elicited strong reactions from global leaders. In Greenland, the current Prime Minister emphasized the territory’s autonomy, declaring,
“We are not for sale and cannot simply be taken.”
This response underscores the sensitive nature of discussions surrounding Greenland’s status and the potential implications of U.S. interest in the territory.
Similarly, Presidential José Raul Mulino of Panama categorically denied Trump’s claims regarding Chinese control of the canal, insisting that the canal remains under Panamanian sovereignty. The heated exchange of statements highlights the delicate balance of power and the need for clear communication among nations regarding territorial rights and engagement.
Internationally, analysts are closely monitoring how these developments may reshape not only U.S. relations with Greenland and Panama but also the broader geopolitical landscape in the Arctic and Latin America. Concerns about potential resource competition and military presence have made these regions focal points of international diplomacy and strategy.
Historical Context of U.S. Interests in Greenland
The historical context of U.S. interests in Greenland dates back to World War II when the U.S. established its first military base on the island. The Greenlandic territory has a complicated history of colonization that began in the early 18th century with the Kingdom of Denmark. However, the geopolitical landscape shifted significantly during the war, when then-Danish Ambassador Henrik Kauffmann defied orders from Nazi-occupied Denmark and reached an agreement with the U.S. to defend Greenland.
Following Denmark’s liberation from Nazi rule, the U.S. maintained its military presence on the island, emphasizing the region’s strategic importance. Greenland’s Pituffik Space Base remains the northernmost U.S. military installation and is considered valuable for monitoring not only Arctic activities but also broader global security threats. Trump’s recent focus on Greenland could be seen as an extension of these longstanding U.S. interests.
The Historical Background of the Panama Canal
Constructed by the United States between 1904 and 1914, the Panama Canal has dramatically influenced global trade routes, serving as a vital link between the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. For decades, the canal was operated by the U.S. government, leading to tension between the U.S. and Panama over issues of sovereignty and control. In the 1970s, a treaty was established that outlined the canal’s permanent neutrality and assured Panama’s eventual control.
By the end of the 20th century, the canal’s control was fully transferred to Panama. The Panama Canal Authority now manages this crucial infrastructure, which plays a key role in international maritime commerce. It is critical to note that Trump’s recent remarks have reignited discussion about U.S. interests in the canal, set against the backdrop of historical tensions and negotiations regarding its operation.
| No. | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | President Trump reiterated the U.S. need for Greenland and the Panama Canal during his address to Congress. |
| 2 | Greenland’s strategic location and wealth of resources make it significant for U.S. national security. |
| 3 | Controversial claims by the President have drawn sharp rebukes from both Greenland and Panama’s leaders. |
| 4 | Historical connections between the U.S., Greenland, and the Panama Canal stem from geopolitical interests and treaties. |
| 5 | Responses to U.S. claims underscore the sensitivities around territorial sovereignty and international diplomacy. |
Summary
The recent comments made by President Trump regarding Greenland and the Panama Canal reveal not only his administration’s ambitions but also the complex geopolitical web surrounding these territories. As the U.S. grapples with transitioning global dynamics, the reactions from leaders in Greenland and Panama showcase the potential for conflict as well as the importance of diplomatic efforts to ensure stability and respect for sovereignty. The focus on Greenland’s strategic resources and the Panama Canal’s critical role in trade emphasizes the broader economic implications of these discussions, which will undoubtedly continue to evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Why does the U.S. want Greenland?
Greenland is strategically located and rich in natural resources, making it vital for U.S. national security and economic interests, especially as new shipping routes emerge due to climate change.
Question: What role does the Panama Canal play in global trade?
The Panama Canal is a critical shortcut for shipping between the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean, handling about 40% of U.S. container traffic and significantly impacting international trade efficiency.
Question: How have global leaders reacted to Trump’s claims on Greenland and Panama?
Leaders from both Greenland and Panama have firmly rejected Trump’s assertions, emphasizing their sovereignty and sovereignty over these territories while stressing that they are not for sale or controlled by foreign powers.